

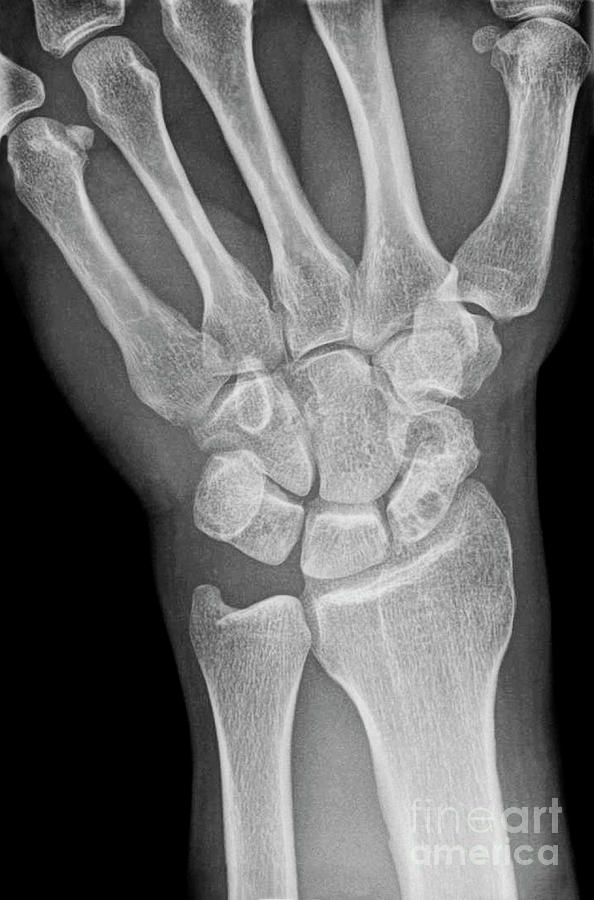
The most common operative technique is using a percutaneous variable-pitched screw, which can be placed across the fracture site to compress it. However, undisplaced fractures of the proximal pole have a high risk of AVN and surgical treatment may be advocated, particularly if it is the dominant hand of a working-age patient.Īll displaced fractures should be fixed operatively. Undisplaced fractures can typically be managed with strict immobilisation in a plaster with a thumb spica splint. The treatment of scaphoid fractures is determined by location of the fracture and degree of the fracture. Figure 3 - (A) Initial AP radiograph showing a subtle linear lucency within the scaphoid (B) more pronounced lucency observed in repeat imaging after 12 days Management This is the definitive investigation and, whilst it is awaited, the interim management is as for a fracture. If repeat radiographic imaging is negative, however clinical findings are still in keeping with a scaphoid fracture, an MRI scan of the wrist is indicated. Scaphoid fractures are not always detected by initial radiographs (especially undisplaced fractures) if there remains sufficient clinical suspicion, despite negative initial imaging, the patient should have the wrist immobilised in a thumb splint and repeat plain radiographs in 10-14 days for further evaluation (Fig. A “ scaphoid series” should be requested, including anteroposterior, lateral, oblique views. Investigationsįor suspected cases of scaphoid fracture, initial plain radiographs should be taken. The main differentials of radial wrist pain following trauma are distal radial fracture, an alternative carpal bone fracture, fracture of the base of the 1 st metacarpal, ulnar collateral ligament injury, wrist sprain, or De Quervains tenosynovitis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
